DIURETICS | PHARMACOLOGY | GPAT-2020 | PHARMACIST
Visit our website :- http://www.gdc4gpat.com
Download GDC App:- https://goo.gl/uaGsY2
Join GDC Online Test:- http://www.gdconlinetest.in/
FACEBOOK- https://www.facebook.com/GPATDISCUSSION/
INSTAGRAM- https://www.instagram.com/gpat_discus…
TWITTER- https://twitter.com/GPAT_Discussion
Pharmacology Tips Loop Diuretics Lasix
EmpoweRN.com
Thank you so much for watching my channel!
For the additional resources you can visit here:
http://empowern.com/2015/03/pharmacology-loop-diuretics-lasix/
Also, to enter the giveaway all you have to do is:
1. Post a comment
2. Subscribe to the channel.
Winner will be announced via email here:
http://goo.gl/NO7T7b
I would like to thank the video contributors:
Rizalyn Joy Gadugdug
Maria Salvacion Gonzales
Yasmin Hashmi
Artem Shestakov
And Babar Hayatrana
Disclaimer:
These videos are intended for entertainment purposes only. Please follow the policy and procedures that your institution requires.
Please note that the views, ideas & opinions expressed on this channel and in the videos on this channel are not necessarily of those of my employer or institution. The views expressed on this channel and in the videos channel do not represent medical advice. If you have specific medical concerns, please contact your physician. In order to protect patient privacy, all patient identifiers in all videos have been deleted or altered.
The views expressed on this channel and in the videos on this channel are personal opinions. I am not an expert nor do I dispense medical advice or procedural specifications. The information I present is for general knowledge and entertainment purposes only. You need to refer to your own medical director, teachers and protocols for specific treatment information. It is your responsibility to know how best to treat your patient in your jurisdiction.
Furosemide (Lasix) – Loop Diuretics
Generic Name: Furosemide
Brand Name: Lasix
Furosemide also known as Lasix is a loop diuretic commonly use to treat fluid retention and edema. Which can be associated with Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), cirrhosis of the liver, and many kidney disorders. It is also sometimes use to treat hypertension alone or in combination with other anti-hypertensive drugs.
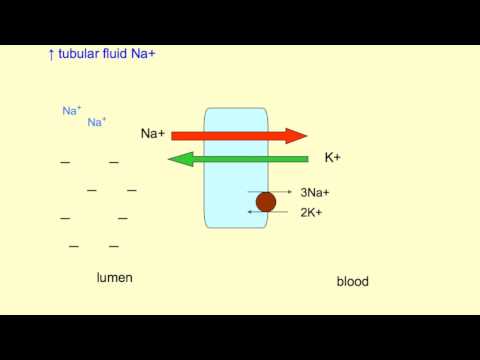
Diuretics are medications that increases the amount of water that passes through the kidneys as urine, thus, it is often called water pill. Lasix belongs to the group known as Loop diuretics. There a few types of diuretics and loop diuretics are just one type. It works by interfering with the sodium, potassium and chloride symporter. A symporter is a protein membrane that manages the transport of molecules across a cell membrane. The symporter that lasix interacts with is found in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. What it does is………. inhibits the reabsorption of salt (Na+) and Chloride (Cl-). Since the Salt and Chloride will be leaving the body system through the loop of henle this means that water will also follow…. causing more water pass through the kidney. Which will ultimately mean, less fluid remaining in the blood stream.
Once Lasix is received the system will then compensate the loss by absorbing any fluid accumulated in the tissues, such as in the lungs or legs, back to the blood stream.
This will cause more fluid to be in the blood stream. Which once again pass through the kidney, which will also be excreted in the urine, since the loop diuretic inhibits its reabsorption.
This mechanism, is what makes loop diuretics a treatment for fluid retention also known as edema. It can therefore, ease symptoms of edema such as breathlessness caused by congestion of fluid in the lungs which patients diagnosed with CHF, cirrhosis of the liver, nephrotic syndrome and other edematous states may encounter.
Lasix is available in forms that can be taken orally and intravenously. When taken intravenously, it is considered to be twice as strong.
Parenteral or intravenous Furosemide is indicated when a fast acting and an intense diuresis is needed such as in acute pulmonary edema and cerebral edema. It also indicated when oral therapy is not possible because of problem with absorption in the intestine or for other reasons. Parenteral administration should be observed only in hospital or outpatient clinics. However, in cases of emergency that furosemide should be given right away outside hospital setting, recommended doses should be closely adhered to and patient must be closely monitored.
Contraindication:
Furosemide should not be taken if your patient cannot urinate.
Severe Hypokalemia – is a major contraindication. This means low potassium. Lasix can cause a dramatic decrease in potassium level which could cause lethal cardiac arrhythmias
Other contraindications include:
Hypotension or low blood pressure
Lasix should be used with extreme caution for patients who have a diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus because it may May
DIURETICS PHARMACOLOGY | PHARMACOLOGY | GPAT-2020 | NIPER | PHARMACIST
In this video we are providing DIURETICS PHARMACOLOGY, which is very important for the GPAT, NIPER, Drug Inspector, Pharmacist, NEET Examination.
If you like this video like it comment it and subscribe it and share with your friends.
Visit our website :- http://www.gdc4gpat.com
Download GDC App:- https://goo.gl/uaGsY2
Join GDC Online Test:- http://www.gdconlinetest.in/
FACEBOOK- https://www.facebook.com/GPATDISCUSSION/
INSTAGRAM- https://www.instagram.com/gpat_discus…
TWITTER- https://twitter.com/GPAT_Discussion
Dr. Puspendra Classes Videos – https://www.youtube.com/user/puspendra007
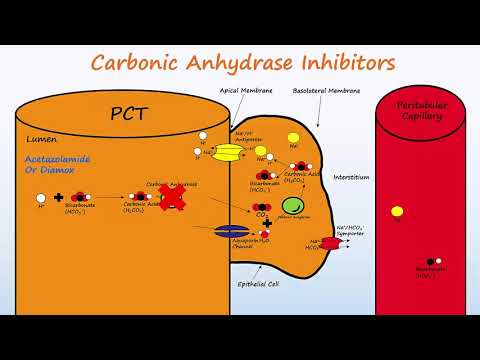
Diuretics – Part 1 – Osmotic Diuretics & Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Explains the mechanisms of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and osmotic diuretics. Also discusses indications for the medications.
RENAL PHARMACOLOGY 7:ADH (Anti-diuretics Hormone / Vasopressin ) Agonists and Antagonists
ADH or anti diuretic hormone or vasopressin is the main hormone responsible for the volume of urine which is excreted and since its a hormone , we have both agonists and antagonists i.e. both ways to potentiate its action or to negate its action .
NEET PG | Pharmacology | Diuretics Part – 1 | Unacademy | by Siraj Ahmad
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z3WUPeTllKQ
All the diuretics acting on a different part of nephron and their uses will be discussed.
Unacademy Plus: https://unacademy.com/plus/goal/SDDOC
Use code “sirajahmad9” for 10% discount.
Unacademy Plus Subscription Benefits:
1. Learn from your favorite teacher
2. Dedicated DOUBT sessions
3. One Subscription, Unlimited Access
4. Real-time interaction with Teachers
5. You can ask doubts in the live class
6. Download the videos & watch offline
#Unacademy #UnacademyNEETPG #NEETPG2020
Free Water Clearance and diuretics pharmacology for NEET/USMLE/FMGE/PLAB
Free Water Clearance and diuretics for NEET/USMLE/FMGE/PLAB
Free Water Clearance:
• Free water clearance is the amount of solute free water generated by the kidney.
• This solute free water is generated in the thick ascending limb and distal convoluted tubule, which are permeable to solutes but impermeable to water. Thus, this solute free water generated in the lumen is called as positive free water clearance.
• Solutes absorbed in thick ascending limb gives rise to medullary hyperosmolarity which absorbs the free water in collecting duct in response to vasopressin. Thus, here solute free water moves out from the lumen in to the body and this is known as negative free water clearance.
• Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamide) deliver more Na+ and water to thick ascending limb and distal convoluted tubule, where only Na+ is absorbed and water remains in lumen. Thus there is an increase in positive free water clearance.
• Loop diuretics (furosemide) and thiazides (chlorothiazide) inhibit Na+ absorption and hence there is more Na than before in lumen as compared to water. Hence loop diuretics and thiazides decrease positive free water clearance.
• Loops decrease Na+/Cl- absorption in thick ascending limb and thus there is a decrease in medullary hyperosmolarity. This decreases absorption of solute free water from the lumen of collecting duct in to the body. Hence loop diuretics decrease negative free water clearance as well.
RENAL PHARMACOLOGY 6:Potassium Sparing Diuretics
All the renal drugs we have seen so far lead to hypokalemia and so this group of drugs were introduced to prevent that condition from occurring and are now these drugs are widely used in combination with the other diuretics as a very to increase the beneficial effects of the initial diuretics and prevent potassium loss
Heart Failure | Pharmacology (ACE, ARBs, Beta Blockers, Digoxin, Diuretics)
Free Quiz & full course for heart failure drugs: https://Simplenursing.com/nursing-school
Pharmacology treatment of Congestive Heart Failure includes:
– Ace inhibitors: Lisinopril, Captopril (1:39)
– Beta Blockers: Atenolol, Carvedilol (5:06)
– Calcium Channel Blockers: Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Verapamil (8:02)
– Digoxin | Cardiac Glycoside (11:14)
– Diuretics l Loop diuretics, Thiazide diuretics, Potassium Sparing diuretics: Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide, Spironolactone (18:08)
Frustrated with boring NCLEX programs “included” in your tuition? Check out the SimpleNursing NCLEX prep mobile app: https://simplenursing.com/free-trial/
– Over 2,000 NCLEX style questions
– Visual in-depth rationals
– 1,200 fun videos & 300 Cheat Sheets covering the most highly tested topics
– Test tips & Memory Tricks included
– 92% pass rate | learn how: https://simplenursing.com/free-trial/
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUxQWmWk1_Hk9iDRKvhH29Q?sub_confirmation=1
Need help with other difficult nursing school topics? Click below. We got you covered 🙂
– Fluid & Electrolytes https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnLJSqeCM_EJHXZ685sb67bn
– Heart Failure (CHF) https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnLEVzZvkdBX1IWHPg21Jobw
– Myocardial Infarction (MI) https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnLLJQsAIsQaHJiOvcLN1cUe
– Addison’s vs. Cushing https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnKT3JBkVTN-hXbyULbPgWz5
– Diabetes Mellitus & DKA vs HHNS https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnKxNrh1HdilzIIH9WM8JrLq
– Cardiomyopathy https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnIeh0g_moaGLzXWiOh3fqdi
– IV Fluids: Hypertonic, Hypotonic & Isotonic https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3NAm8UHLUnIdjUfgMcAE1JIq6Nx29JRX
– Hypertension https://youtu.be/5zg95R8H1oo
– Hyperkalemia https://youtu.be/HdG8lqJzWi4
– SIADH vs Diabetes Insipidus https://youtu.be/hKFGGv0E-5A
Follow me on Social Media:
– Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/SimpleNursing
– Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/simplenursi…
– Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/SimpleNursing
– Like us on Facebook: https://facebook.com/SimpleNursing
Thanks for tuning in.
Don’t be scared, BE PREPARED!
#CHFdrugs #HeartFailure #BetaBlockers #Diuretics #AceInhibitors #Pharmacologynursing