NEET PG | Pharmacology | Diuretics Part -II for NEET PG by Siraj Ahmad
Diuretics part 2 I will be discussing the diuretics acting at loop of Henle i.e. loop diuretics, Thiazide diuretics and potassium sparing diuretics along with their uses in different conditions and their important side effects. These are frequently asked drugs and topics in NEET PG.
Unacademy Plus: https://unacademy.com/plus/goal/SDDOC
Use code “sirajahmad9” for 10% discount.
Unacademy Plus Subscription Benefits:
1. Learn from your favorite teacher
2. Dedicated DOUBT sessions
3. One Subscription, Unlimited Access
4. Real-time interaction with Teachers
5. You can ask doubts in the live class
6. Download the videos & watch offline
#Unacademy #UnacademyNEETPG #NEETPG2020
High Ceiling Diuretics- MOA ,ADR,USES,DRUG DOSE (Diuretics part 2)
This video is all about High ceiling diuretics with complete explanation about the MECHANISM OF ACTION,ADVERSE DRUG REACTION,USES and DOSES of drug given… this video is based on the standard medical pharmacology book reference… i have tried to covered all the basic things of this topic hope you like the video ..
if u liked the video please like share and subscribe my channel so that i could upload more videos like this… i need your support to grow 🙂
#thankyou
#peace
13.Thiazide Diuretics Part 2 – Renal pharmacology
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCG5TBPANNSiKf1Dp-R5Dibg/join
Follow on Instagram:- https://www.instagram.com/drgbhanuprakash
Diuretics are a group of drugs that increase the production of urine. Diuretics are categorized according to the renal structures they act on and the changes they lead to in the volume and composition of urine, as well as electrolyte balance. Some of these effects are useful in treating disorders such as hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia, and hyperaldosteronism. The most commonly used diuretics with a pronounced diuretic effect are thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-sparing diuretics. Osmotic diuretics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used in acute settings to lower intracranial and/or intraocular pressure (e.g., cerebral edema, acute glaucoma). The most serious side effects of the majority of diuretics include volume depletion and excessive changes in serum electrolyte levels (particularly of sodium and potassium), which increases the risk for cardiac arrhythmias.
#thiazidediuretics #thiazides #diureticdrugs #diureticsandtheireffects #loopdiuretics#diuretics #diureticsintroduction #diureticspharmacology #pharmacology #usmle #usmlestep1 #nationalexittest #mbbs #pharmacologyvideos #pharmacology #diureticslecture #uworld
12.Thiazide diuretics part 1 – Renal pharmacology
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCG5TBPANNSiKf1Dp-R5Dibg/join
Follow on instagram :- https://www.instagram.com/drgbhanuprakash
Diuretics are a group of drugs that increase the production of urine. Diuretics are categorized according to the renal structures they act on and the changes they lead to in the volume and composition of urine, as well as electrolyte balance. Some of these effects are useful in treating disorders such as hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia, and hyperaldosteronism. The most commonly used diuretics with a pronounced diuretic effect are thiazides, loop diuretics, and potassium-sparing diuretics. Osmotic diuretics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used in acute settings to lower intracranial and/or intraocular pressure (e.g., cerebral edema, acute glaucoma). The most serious side effects of the majority of diuretics include volume depletion and excessive changes in serum electrolyte levels (particularly of sodium and potassium), which increases the risk for cardiac arrhythmias.
#thiazidediuretics #thiazides #diureticdrugs #diureticsandtheireffects #loopdiuretics#diuretics #diureticsintroduction #diureticspharmacology #pharmacology #usmle #usmlestep1 #nationalexittest #mbbs #pharmacologyvideos #pharmacology #diureticslecture #uworld
PHARMACY| PHARMACOLOGY- DIURETICS & ANTI-DIURETICS
PHARMACOLOGY-
THIS VIDEO CONTAIN IMPORTANT MCQS ON DIURETICS & ANTI-DIURETICS .This video will be very helpful for those who is preparing for the pharmacist competitive exams like government pharmacist,gpat, niper, drug inspector, prometric etc. in coming videos you can expect different videos chapter-wise. So kindly watch this video completely and if you like this video press the subscription button.
WATCH MORE BY SUBSCRIBING CHANNEL: https://bit.ly/2SOfqdN
NS Pharma Youtube platform: https://bit.ly/35ekjzy
Important Pharmacology Questions: https://bit.ly/2FaVJEN
PHARMACIST DEMO MOCK TEST-1: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_U0_qd9ULkE
PHARMACIST DEMO MOCK TEST-2: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4cQc6i4DV-A
PHARMACIST DEMO MOCK TEST-3: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N_DjBiHCZj0
PHARMACIST DEMO MOCK TEST-4: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-cCJH_4rNrs
PHARMACIST DEMO MOCK TEST-5: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wS_hAYZwqD4&t=120s
PHARMACIST DEMO MOCK TEST-6: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WnS7hv0daIw&t=13s
thank you
NS Pharma
Pharmacology 650 a High Ceiling Loop Diuretics Furosemide Frusemide Mechanism of Action
#HighCeiling #LoopDiuretics #Furosemide Frusemide Mechanism of Action
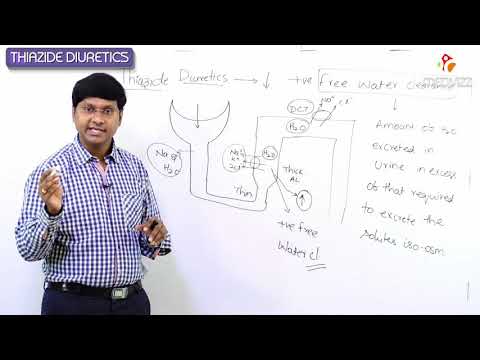
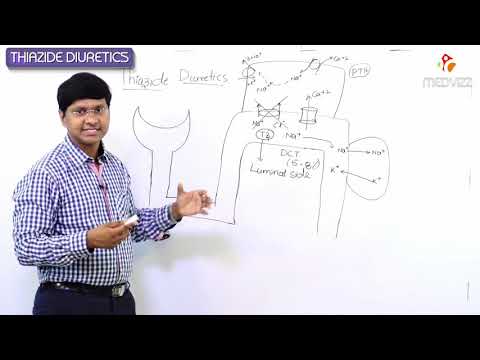
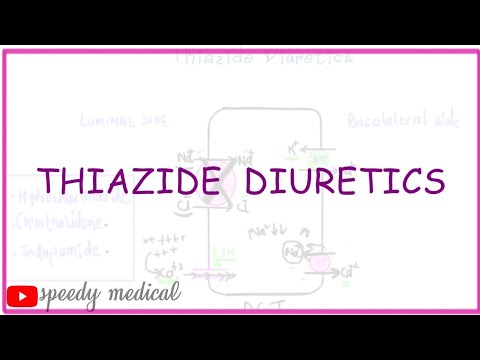
Diuretics- Thiazide Diuretics.Pharmacology of Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics (water pills) are medications that are used to treat highblood pressure (hypertension) and reduce fluid accumulation in the body. They work by reducing the ability of the kidneys to reabsorb salt and water from the urine and into the body thereby increasing the production and output of urine (diuresis).
The examples are chlorthalidone (Thalitone)
hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
methyclothiazide
Thiazide diuretics are used to treat high blood pressure and congestive heartfailure as well as the accumulation of fluid and swelling (edema) of the body caused by conditions such as heart failure,cirrhosis, chronic kidney failure,corticosteroid medications, and nephrotic syndrome.
Side effects of thiazide diuretics are dose related and include:
dizziness and lightheadedness,
blurred vision,
loss of appetite,
itching,
stomach upset,
headache, and
weakness.
Diuretics mechanism of action, uses | Renal Physiology | Pharmacology
Diuretics are substances which increase the flow rate of urine. Most of the classes of diuretics work by increasing both the solute as well as water loss.
1. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: They inhibit the carbonic anhydrase enzyme present in epithelial cells lining the proximal convultae tubule. Thus, they decrease the reabsorptionof sodium as well as that of bicarbonate. Due to this, there is decrease in pH causing metabolic acidosis. They ae used mianly to block carbonic anhydrase enzyme in eyes especially in open angle glaucoma and in high altitude sickness where they prevent the development of metabolic alkalosis.
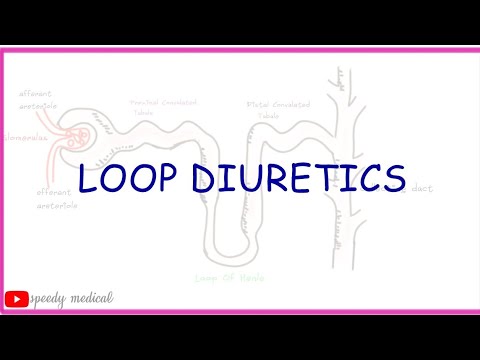
2. Loop diuretics: Loop diuretics inhibit sodium potassium 2cl- transporter. This interefers with both the concentration as well as dilution of urine. They are very effective diuretics since they interfere with absorptiono f approximatelu 25% of sodium reabsorptionin nephron.
3. Thiazide diuretics: These diuretics act on distal convulated tubule where they block sodium chloride symporter. They mainly interfere with dilutionof urine and not with concentrationo f urine. They are moderately effective diuretics which interfere with 5-10% of reabsorption of filtered sodium.
4. Potassium sparing diuretics: They act on late distal tubule and collecting ducts. They act by inhibiting either epithelial sodium channels or mineralocorticoid receptors. They are not very effective diuretics as such but when combined with other diuretics, they help in preventing the development of hypokalmeic alkalosis.
5. Osmotic diuretics. Osmotic diuretics interfere mainly with reabsorption of water and not of solutes.Osmotic diuretics, are filtered from the glomerulus but are not absorbed and tend to remain in the tubular fluid. Hence,in descending limb of loop of henle which is permeable to water, they prevent the movement of water out from tubular lumen since they exert on osmotic pull on water.
#diureticspharmacology
#renalpharmacology
#renalphysiology
#physiologyopen
Diuretics-Loop Diuretics Pharmacology
Loop diuretics are diuretics that act at the ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidney. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure or chronic kidney disease. While thiazide diuretics are more effective in patients with normal kidney function, loop diuretics are more effective in patients with impaired kidney function.
. Loop diuretics act on the Na+-K+-2Cl− symporter (NKCC2) in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle to inhibit sodium, chloride and potassium reabsorption. This is achieved by competing for the Cl− binding site. Loop diuretics also inhibits NKCC2 at macula densa, reducing sodium transported into macula densa cells. This stimulates the release of renin, which through renin–angiotensin system, increases fluid retention in the body, increases the perfusion of glomerulus, thus increasing glomerular filtration rate (GFR). At the same time, loop diuretics inhibits the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism so that increase in salts at the lumen near macula densa does not trigger a response that reduces the GFR.