Diuretics – Mechanism of Action of Different Classes of Diuretics, Animation
Pharmacology of diuretics: Mechanism of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, osmotic diuretics, loop diuretics, thiazides , and potassium-sparing diuretics. This video is available for instant download licensing here https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/all-animations/urinary-system-videos/-/medias/b1eb96d4-a43e-4fdb-af86-dd0149a1e37d-diuretics-narrated-animation
Voice by: Ashley Fleming
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Support us on Patreon and get early access to videos and free image downloads: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition
Diuretics are commonly used to treat primary hypertension and edema. Changes in body fluid and electrolytes induced by diuretics can also be therapeutic for some other conditions.
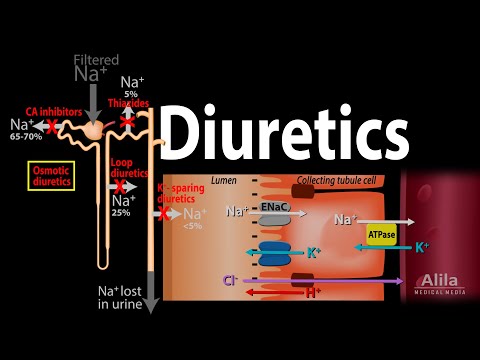
Sodium and water are filtered in the glomerular capsule of nephrons, then reabsorbed back to the blood at various sites along the renal tubule. Different classes of diuretics prevent sodium reabsorption, and thus increase sodium loss, at different sites, by different mechanisms.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors inhibit the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which is required for reabsorption of bicarbonate in the proximal tubule. Most of sodium lost at this early stage is reclaimed further down the renal tubule. Increased delivery of sodium to the collecting duct increases its reabsorption at this site through epithelial sodium channels, in exchange for a greater potassium loss, and may cause hypokalemia. Loss of bicarbonate also affects acid-base balance, producing metabolic acidosis. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are rarely prescribed for cardiovascular diseases; they are mainly used in the treatment of glaucoma.
Osmotic diuretics, such as mannitol, promote water loss directly through osmosis. Mannitol is effective in lowering intracranial pressure in patients with head injury, and lowering intraocular pressure in acute glaucoma.
Loop diuretics inhibit the sodium/potassium/chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. These are very powerful diuretics because this transporter not only reabsorbs a large share of sodium, but is also responsible for the osmolarity gradient in the medulla that enables the collecting duct to concentrate urine. Side effects include electrolyte imbalances, metabolic alkalosis, hypovolemia due to excessive loss of water, loss of hearing due to inhibition of a similar transporter in the inner ear, and gout due to interference with transporters involved in urate secretion.
Thiazide diuretics inhibit the sodium/chloride cotransporter in the distal tubule, which reabsorbs about 5% of the sodium load, and are not as powerful as loop diuretics. However, thiazides also have a vasodilation effect by a still poorly understood mechanism. Thiazides are first-line drugs for uncomplicated hypertension and most effective for heart failure prevention.
Unlike loop diuretics, thiazides reduce calcium loss in urine and can be used to prevent formation of new calcium kidney stones. This is because lower intracellular sodium induced by thiazides leads to higher calcium reabsorption mediated by sodium/calcium exchanger located on the basolateral membrane. Other side effects are similar to those of loop diuretics and include hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis and hyperuricemia.
Potassium-sparing diuretics act mainly in the collecting duct. Here, sodium reabsorbs through epithelial sodium channels, ENaC, then sodium/potassium pump, in exchange for potassium loss. Sodium influx into cells creates a negative lumen potential, which drives reabsorption of chloride and excretion of potassium and hydrogen. Both ENaC and sodium/potassium pump are induced by aldosterone.
Potassium-sparing diuretics include aldosterone receptor antagonists and direct ENaC inhibitors. They are called potassium-sparing because they do not increase potassium loss, unlike all other diuretics acting upstream. Instead, they reduce potassium loss because reduced sodium reabsorption decreases the electrogenic exchange for potassium. Aldosterone antagonists also directly inhibit the sodium/potassium pump, reducing potassium loss.
Because the collecting duct reabsorbs only a small amount of sodium, this class of drugs has only a mild diuretic effect. They are commonly used in conjunction with thiazide or loop diuretics to prevent hypokalemia. Side effects include hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, and effects associated with inhibition of aldosterone.
Pharmacology – Diuretics – Part 1/3
Like this video? Sign up now on our website at https://www.DrNajeebLectures.com to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now and get 95% OFF! Get Lifetime Access for a one-time payment of $5 ONLY!
Why sign up for premium membership? Here’s why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that’s 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
Thiazide Diuretics Pharmacology Nursing NCLEX Review (Mechanism of Action & Side Effects)
Thiazide diuretics pharmacology nursing NCLEX review about the mechanism of action, side effects, nursing implications, and patient education.
Thiazide diuretics work to inhibit the sodium-chloride cotransporter (NCC) in the early part of the distal convoluted tubule. This will decrease sodium reabsorption…meaning less sodium will enter back into the blood. Instead, the sodium will stay in the filtrate. Therefore, this will cause more water to stay in the filtrate and less to be reabsorbed back into the blood…hence, leading to diuresis (increased urination).
Thiazides are used to treat hypertension, heart failure, and renal calculi that are composed of calcium.
Side effects of thiazides include hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia, hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and orthostatic hypotension.
Nursing implication for thiazide diuretics are monitoring for signs and symptoms of dehydration (low blood pressure, fast heart rate), strict intake and output measure, daily weights, monitor labs for electrolyte imbalances, avoid digoxin and lithium toxicity etc.
#diuretics #thiazides #pharmacologynursing
Quiz: https://www.registerednursern.com/thiazide-diuretics-pharmacology-nclex-questions/
Notes: https://www.registerednursern.com/thiazide-diuretics-pharmacology-nclex-review/
More Pharm Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWpel1Ymwd9IQe0noyzAjeS
Website: https://www.registerednursern.com/
Nursing Gear: https://teespring.com/stores/registerednursern
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/registerednursern_com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RegisteredNurseRNs
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NursesRN
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWtwCDmLHyX2UeHofCIcgo0
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWJSZ9pL8L3Q1dzdlxUzeKv
Nursing Skills: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfUhd_qQYEbp0Eab3uUKhgKb
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Pharmacology Nursing (Mechanism of Action) Review
Potassium-sparing diuretics pharmacology review for nursing students in preparation for the NCLEX exam.
This review will discuss the mechanism of action of potassium-sparing diuretics, what conditions they treat, nursing responsibilities, side effects, and patient education.
Potassium-sparing diuretics inhibit the sodium channels in the last parts of the nephron, specifically the last part of the distal tubule and the collecting duct. When sodium channels are inhibited this will decrease the sodium and potassium exchange via the sodium-potassium pump within the nephron. This will cause sodium to stay in the filtrate instead of being reabsorbed, which causes water to stay with the sodium and this achieves the diuretic effect. Furthermore, this will limit potassium from leaving the bloodstream to enter the filtrate (hence SPARING potassium…this can lead to hyperkalemia in some patients).
There are two types of diuretics I discuss in this video: epithelial sodium channel inhibitors (Triamterene and Amiloride) and aldosterone antagonist (Spironolactone and Eplerenone).
Side effects of potassium-sparing diuretics include: hyperkalemia, dehydration, antiandrogen effects like gynecomastia, menstrual problems, decrease sex drive, upset stomach
Nursing interventions include: monitoring for dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, educating about limiting foods high in potassium/salt-substitutes, medication interactions with ACEI, ARBs, NSAIDs and Lithium etc.
#potassiumsparingdiuretics #diuretics #pharmacologynursing
Quiz: https://www.registerednursern.com/potassium-sparing-diuretics-nclex-questions-pharmacology/
Notes: https://www.registerednursern.com/potassium-sparing-diuretics-pharmacology-nclex-review/
More Diuretic Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfVvu5KuxwaMbz8ajjH_vIj5
More Pharmacology Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWpel1Ymwd9IQe0noyzAjeS
Nursing Gear: https://teespring.com/stores/registerednursern
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/registerednursern_com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RegisteredNurseRNs
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NursesRN
Website: https://www.registerednursern.com/
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWtwCDmLHyX2UeHofCIcgo0
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWJSZ9pL8L3Q1dzdlxUzeKv
Nursing Skills: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfUhd_qQYEbp0Eab3uUKhgKb
Diuretics in 3 Minutes! [Pharmacology]
Please watch: “Video Course for FINAL MEDICAL EXAMS!”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H0oETfpRllA –~–
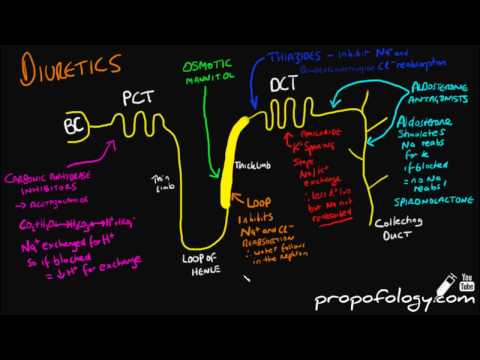
Where oh where do diuretics act in the nephron? A very common medical school and post graduate question, this VERY short video goes through all the major classes of diuretics and explains clearly WHERE and HOW they work to induce a diuretic effect.
A key concept is understanding that when SODIUM stays INSIDE the nephron tubules (and is NOT reabsorbed back into the body) it carries water with it, which is excreted. Nearly all the diuretics work by this principle.
Used widely in the community, hospitals and ICU, diuretics are an incredibly common medication – so you WILL be asked about them in nearly every specialty medical exam.
Find out more on www.propofology.com/resources and find Diuretics in the resource links with my full infogram on the topic!
Diuretics – Pharmacology (EXPLAINED)
Like this video? Sign up now on our website at https://www.DrNajeebLectures.com to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now and get 95% OFF! Get Lifetime Access for a one-time payment of $5 ONLY!
Why sign up for premium membership? Here’s why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that’s 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
Nursing pharmacology video 17 – Diuretics
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G7JMCkw_Qkw
Cathy Parkes RN, covers Nursing pharmacology – Diuretics. The Nursing pharmacology video tutorial series is intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
Please offer comments or suggestions on how these videos can be improved! Also, please feel free to share these videos with your classmates 🙂
Cathy’s Nursing Pharmacology Flashcards are available at http://bit.ly/pharmacards
🚨GET MORE RESOURCES, TIPS AND STUDY AIDS! 🚨
https://www.leveluprn.com/
👇SHOP MY STUDY CARDS👇
📚All of My Study Cards:
https://www.leveluprn.com/collections/available-now
📓Medical Surgical Study Cards:
Medical-Surgical Nursing – Flashcards
📕Pharmacology Study Cards:
Pharmacology – Nursing Flashcards
📗Nursing Fundamentals Study Cards:
http://bit.ly/fundacards
📙Nutrition Study Cards:
http://bit.ly/nutricards
📘Community Health Study Cards:
http://bit.ly/commcards
➡️ CATHY’S PICKS ON AMAZON ⬅️
My favorite products available on Amazon to help you advance your career.
https://www.amazon.com/shop/cathyparkes
👩⚕️ HI I’M CATHY PARKES 👩⚕️
I’m here to help you Level Up! During my time at CSUSM’s Accelerated Bachelor’s of Nursing program, I helped my fellow classmates who were struggling with the exam, pass and graduate. After receiving my BSN I went on to become an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital. As more and more students reached out to me for help, I decided to start this channel to help people across the world, LEVEL UP.
👋 STAY CONNECTED 👋
Facebook: https://fb.me/LevelUpRN
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/leveluprn/
—————————
DISCLAIMER: Some links in the description are affiliate links, meaning that if you buy from those links, I will receive a small commission. This helps support the channel and allows me to continue making more videos like this one. Thank you so much for the support!
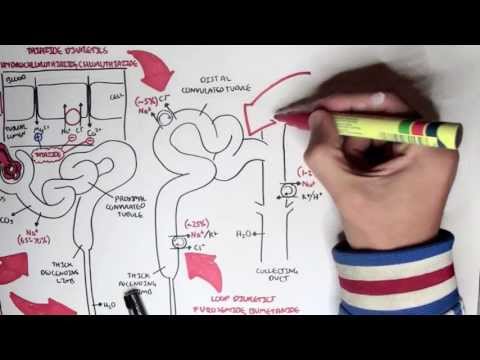
Loop Diuretics Pharmacology Nursing (Mechanism of Action) Furosemide
Loop diuretics pharmacology nursing review that includes the mechanism of action, side effects, nursing interventions, and patient education.
Loop diuretics mechanism of action is on the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. These medications will inhibit the sodium-potassium-chloride (NKCC2) cotransporter. When this cotransporter is inhibited, it will decrease the ions (sodium, potassium, and chloride) reabsorbed into the blood.
In turn, this will decrease sodium reabsorption in the loop of Henle (which normally reabsorbs about 25% of sodium) and decrease the tonicity of the medulla, which is normally hypertonic. The end result will be that the collecting ducts and loop of Henle will reabsorb less water back into the blood and more water will leave the nephron as filtrate.
Side effects of loop diuretics include: hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, ototoxicity, metabolic aklaosis, and dehydration.
Loop diuretics are used to treat heart failure, pulmonary edema, hypercalcemia, and liver impairment (due to ascites).
Nursing interventions for loop diuretics: included in the video.
#loopdiuretics #diuretics #pharmacologynursing
Quiz: https://www.registerednursern.com/loop-diuretics-nclex-questions/
Notes: https://www.registerednursern.com/loop-diuretics-nclex-pharmacology-review/
More Pharmacology Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IEuAa41-oQw&list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWpel1Ymwd9IQe0noyzAjeS
Website: https://www.registerednursern.com/
Nursing Gear: https://teespring.com/stores/registerednursern
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/registerednursern_com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RegisteredNurseRNs
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NursesRN
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWtwCDmLHyX2UeHofCIcgo0
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfWJSZ9pL8L3Q1dzdlxUzeKv
Nursing Skills: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQrdx7rRsKfUhd_qQYEbp0Eab3uUKhgKb
Pharmacology – Diuretics
https://www.facebook.com/ArmandoHasudungan
Support me:
http://www.patreon.com/armando
Instagram:
http://instagram.com/armandohasudungan
Twitter:
Tweets by armando71021105
IMAGE: https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B8Ss3-wJfHrpZUxyQnpYM0hXSHM/edit?usp=sharing
Pharmacology – Diuretics (Loops, Thiazide, Spironolactone) for Registered Nurse RN & PN NCLEX
Diuretics Pharmacology by Mike Linares from https://simplenursing.com/membership
Pharmacology Master Class – 100 videos not on YouTube – Try it for Free!
Pharmacology Master Class – Try it for Free: https://simplenursing.com/membership
100 videos not on YouTube
FREE TRIAL to new app + 1,000 videos not on youtube!
https://simplenursing.com/membership
NCLEX FREE TRIAL:
https://simplenursing.com/freetrialnclex/
STAY IN TOUCH 👋
Subscribe: https://bit.ly/37CRttH
Facebook: https://fb.me/simplenursing
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/simplenursing
🚨Get more in our Nursing School Membership.
– 1,000 + Video Library (not on YouTube),
– 300 + Study guides & NCLEX STYLE QUESTIONS
– New App for iphone + Android !
Try it 100% Free https://www.simplenursing.com
NCLEX App for RN & PN – 1,500 questions, visual detailed rationals
A message from Mike Linares, founder of Simplenursing
Since 2012, I started to do mini lectures from my parents in home library, armed with a $30 white board from Walmart & a sock to erase the board. Since then I have created over 1,200 videos, only 20% which live on YouTube, and have helped over 100,000 nursing students pass their NCLEX, HESI, ATI, and Kaplan proctor exams. Thank you for the continued support and love as we strive to help LPN, LVN and RN students become licensed nurses!
There are three different types of Diuretics that nursing students must review and know for their NCLEX and nursing exams. Diuretics are typically classified as either: potassium wasting diuretics (K+ wasting) or potassium sparing diuretics (K+ sparing). Potassium wasting diuretics include Loop diuretics like Furosemide, and bumetanide, as well as thiazide diuretics like HCT hydrochlorothiazide. Potassium sparing diuretics include spironolactone, which is easy to memorize their mechanism of action of blocking aldosterone hormone, since it sounds spironolactone sounds like aldosterone. In this video we cover a diuretic pharmacology nursing review of everything a student nurse must know for their nursing exams, ATI and HESI exit exams, as well as their NCLEX.
Popular Playlists:
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://bit.ly/39BSHXs
Hear Failure (CHF): https://bit.ly/2u5zfDm
Myocardial Infarction (MI): https://bit.ly/3bN9AAk
Addison’s vs. Cushing: https://bit.ly/2STvute
Diabetes Mellitus & DKA vs HHNS: https://bit.ly/37D8nbs
Cardiomyopathy: https://bit.ly/38CwcSg
IV Fluids: Hypertonic, Hypotonic & Isotonic: https://bit.ly/2P45BWx
SIADH vs Diabetes Insipidus: https://bit.ly/2wq6Bhb
Thank you for the support! Don’t be scared, BE PREPARED!
Thanks for tuning in.
Don’t be scared, BE PREPARED!
#RegisteredNurseRN #HeartFailure #pharm #pharmacology #NCLEX #RN #RegisteredNurse
#Diuretics #Furosemide #RN #Antihypertensives #heartfailure #Pharmacologynursing