Hypertension Treatment | Thiazide Diuretics: Antihypertensives
HELP US GET OUR OWN FILMING STUDIO — https://www.gofundme.com/f/ninja-nerd-science
Ninja Nerds,
Join us for our discussion on thiazide and thiazide like diuretics as we continue our lecture series on cardiovascular pharmacology and how to treat Hypertension (HTN). During this lecture Ninja Nerd Science will go into detail on how thiazide and thiazide like diuretics are used to lower and control high blood pressure as well as decrease excess fluid in the body in conditions such as congestive heart failure (CHF).
Support us by purchasing apparel and donating to our PayPal or Patreon! 😄
–Become a Patron of ours and receive the final, high resolution photo of the lecture!
FUNDING
GoFundMe | https://www.gofundme.com/ninja-nerd-science
APPAREL |
Amazon Prime Free Delivery | https://www.amazon.com/Ninja-Nerd-Science/dp/B07N27WLDR/ref=sr_1_1?dchild=1&keywords=ninja+nerd+science&qid=1577670861&sr=8-1
Teespring | https://teespring.com/stores/ninja-nerd
PATREON | https://www.patreon.com/NinjaNerdScience
SOCIAL MEDIA
FACEBOOK | https://www.facebook.com/NinjaNerdScience
INSTAGRAM | https://www.instagram.com/ninjanerdscience
ALSO, check out our Medical channel | Ninja Nerd Medicine!
https://www.youtube.com/ninjanerdmedicine
Diuretics | Pharmacology | Med Vids made simple
In this video, we have explained all the things you need to know about Diuretics.
We are currently in the process of making more videos on Pharmacology and all subjects in medical school. Subscribe to our channel and click the bell icon to get notified as soon as we upload the videos.
Download the lecture slides of this video by clicking the link below :-
https://www.patreon.com/posts/20172561
(You can download our lecture slides by donating $50 or above. Visit our patreon page to know what cool rewards you get by donating us)
MedVidsMadeSimple is a channel which aims to provide free medical education to medical students across the globe. We provide high-yield content in our lecture videos which are very easy to understand.
Help us make more videos by donating through patreon :-
https://www.patreon.com/medvidsmadesimple
Follow us on facebook to get instant updates :-
http://www.facebook.com/medvidsmadesimple/
Follow us on instagram to get access to our cool medical flashcards :-
https://www.instagram.com/medvidsmadesimple1/?hl=en
Follow us on twitter :-
Tweets by MedVids_MS
Follow us on Google+ :-
https://plus.google.com/113431807529755997363
#MedVidsMadeSimple #MedicalLectures #FreeLectureVideos #USMLE #USMLEstep1
Diuretic (Part 06) Thiazide Diuretic= Mechanism of Action (HINDI) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
(1) Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
(2) Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
(3) Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
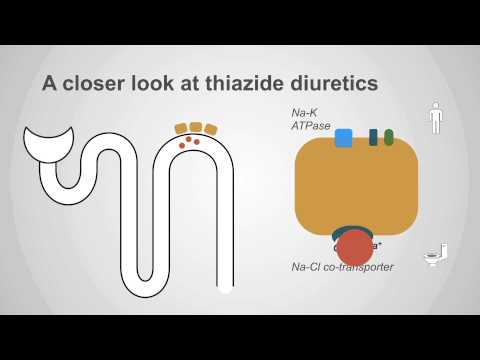
Thiazide diuretics
This is video #3 in our free teaching series on diuretics, this time on thiazide diuretics. The video was taken from our upcoming course on fluids & electrolytes.
Diuretic (Part-03)= Classification of Diuretics with Site of Action (HINDI) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
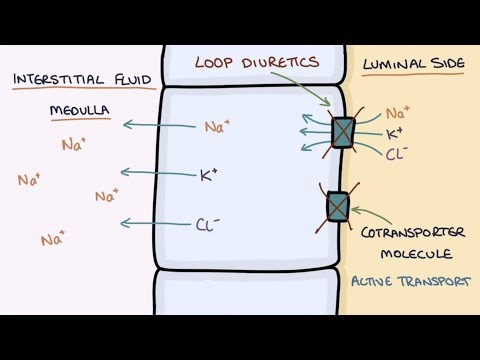
How Does Furosemide Work? Understanding Loop Diuretics
The video contains a simple and visual explanation of how furosemide and bumetanide, loop diuretics, work to encourage the kidneys to excrete more water and sodium. We cover some basics about how the nephron works and look in detail at the action of loop diuretics on the sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter on the ascending loop of the loop of Henle. We also talk about the indications, some practical tips on using loop diuretics, adverse effects and contraindications.
This video is intended to help with the education and understanding of students of healthcare professions only and is not medical advice. For medical advice see your doctor or other healthcare professional. Whilst significant effort has been taken to make the information accurate it cannot be guaranteed.
The Zero to Finals Medicine book is available now to purchase on amazon.
UK: https://www.amazon.co.uk/dp/1091859892
US: https://www.amazon.com/dp/1091859892
Other resources available:
Website: www.zerotofinals.com
Notes: www.zerotofinals.com/learn
Multiple Choice Questions: www.zerotofinals.com/test
Instagram: www.instagram.com/zerotofinals/
Book: www.zerotofinals.com/themedicinemanual
Facebook: www.facebook.com/zerotofinals
Twitter: https://twitter.com/zerotofinals
Diuretic (Part-4) Osmotic Diuretic = Mechanism of Action (HINDI) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
(1) Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
(2) Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
(3) Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
Drugs in Hypertension: Diuretics – Cardiovascular Pharmacology | Lecturio
This video “Drugs in Hypertension: Diuretics” is part of the Lecturio course “Cardiovascular Pharmacology” ► WATCH the complete course on http://lectur.io/diuretics
► LEARN ABOUT:
– Osmotic diuretics
– Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
– Loop diuretics
– Thiazide diuretics
– Potassium sparing diuretics
► THE PROF:
Dr. Shukle is a board certified specialist in internal medicine. He performs over 150 special lectures across the nation each year with various audiences ranging from the general public, to nurses, to physicians, to medical specialists. His lectures are engaging, funny, and informative.
► LECTURIO is your single-point resource for medical school:
Study for your classes, USMLE Step 1, USMLE Step 2, MCAT or MBBS with video lectures by world-class professors, recall & USMLE-style questions and textbook articles. Create your free account now: http://lectur.io/diuretics
► INSTALL our free Lecturio app
iTunes Store: https://app.adjust.com/z21zrf
Play Store: https://app.adjust.com/b01fak
► READ TEXTBOOK ARTICLES related to this video:
Loop Diuretics
http://lectur.io/loopdiuarticle
Thiazide Diuretics
http://lectur.io/hyperdiureticsarticle
Antihypertensives: ACE-Inhibitors and Sartans
http://lectur.io/acearticle
► SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel: http://lectur.io/subscribe
► WATCH MORE ON YOUTUBE: http://lectur.io/playlists
► LET’S CONNECT:
• Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/lecturio.medical.education.videos
• Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/lecturio_medical_videos
• Twitter: https://twitter.com/LecturioMed
Diuretic (Part-01)= Basic Introduction of Diuretics (HINDI) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
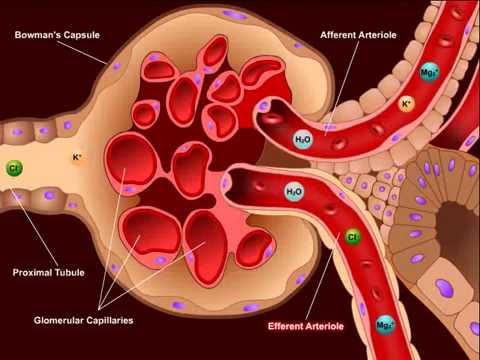
USMLE® Step 1 High Yield: Nephrology: Diuretics
High yield USMLE prep from Kaplan Medical helps you study nephrology, including diuretics and other important exam topics.
Begin your prep for the USMLE – https://www.kaptest.com/usmle
Attend an online event – https://www.kaptest.com/usmle/free/events
Get free USMLE practice – https://www.kaptest.com/usmle/free/usmle-practice
Speak with a Medical Advisor – https://www.kaptest.com/usmle/free/med-advising
Follow us on social media:
Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/KaplanMedical/
Instagram – https://www.instagram.com/kaplanmedical/
Twitter – https://twitter.com/kaplanmedical