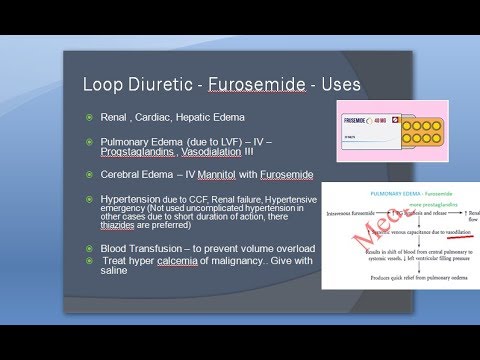
Pharmacology 650 b High Ceiling Loop Diuretic Furosemide frusemide Resistance Uses Adverse Effect
#HighCeiling #LoopDiuretic Furosemide #frusemide Resistance Uses Adverse Effect
Diuretics (pharmacology)
diuretics explained in details with mechanism of action and their uses and side effects explained.
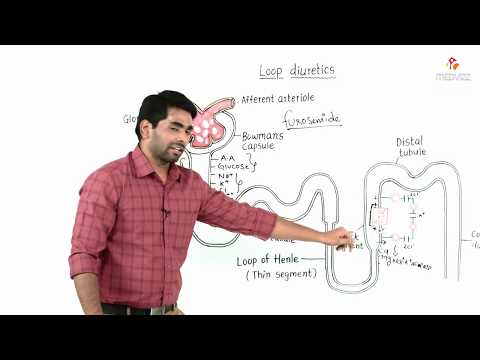
Loop diuretics Mechanism of action : Dr Mahesh
Loop diuretics Mechanism of action
Loop diuretics
A group of drugs that block the Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporters in the thick ascending loop of Henle. This causes the gradient between the renal medulla and cortex to diminish over time and reduces the nephron’s capacity to concentrate the urine, which leads to diuresis. Associated with the following metabolic imbalances: hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hypochloremia, hyponatremia, and metabolic alkalosis.
#loopdiuretics #loopdiureticspharmacology #mechanismofactionofloopdiuretics #loopdiureticsmechanismofaction #diureticspharmacology
Pharmacology – Diuretics – Part 3/3
Like this video? Sign up now on our website at https://www.DrNajeebLectures.com to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now and get 95% OFF! Get Lifetime Access for a one-time payment of $5 ONLY!
Why sign up for premium membership? Here’s why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that’s 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
Diuretic (Part 07) Loop Diuretic (High Ceiling Diuretic) = Mechanism of Action (Hindi)
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
(1) Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
(2) Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
(3) Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
Diuretics/Introduction to diuretics/Classification/Therapeutic indications/side effects of diuretics
Renal Pharmacology – 02 – Loop diuretics and thiazides
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdUqhak8I3E
Video lectures in clinical pharmacology by Dr. Abdel-Motaal Fouda, associate professor of clinical pharmacology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine. 2016.
foudaamm@mans.edu.eg
Diuretic (Part 02)= Parts and Functions of Nephron (HINDI) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest