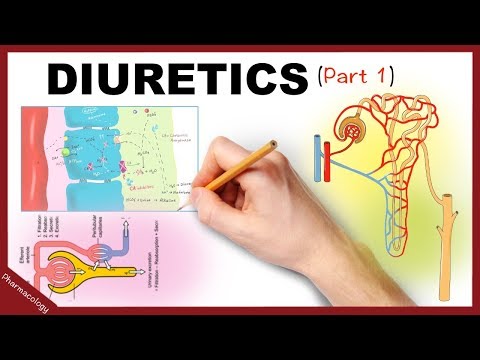
How do Thiazide Diuretics Work? Understanding Bendroflumethiazide and Indapamide
The video contains a simple and visual explanation of how bendroflumethiazide and indapamide, both thiazide diuretics, work to encourage the kidneys to excrete more water and sodium. We cover some basics about how the nephron works and look in detail at the action of thiazide diuretics on the thiazide sensitive sodium chloride co transporter molecule in the distal tubule of the nephron. We also talk about the indications, some practical tips on using thiazide diuretics, adverse effects and contraindications.
This video is intended to help with the education and understanding of students of healthcare professions only and is not medical advice. For medical advice see your doctor or other healthcare professional. Whilst significant effort has been taken to make the information accurate it cannot be guaranteed.
The Zero to Finals Medicine book is available now to purchase on amazon.
UK: https://www.amazon.co.uk/dp/1091859892
US: https://www.amazon.com/dp/1091859892
I love creating resources to help medical students with their studies.
Why not have a look at some of the other resources available:
Website: www.zerotofinals.com
Notes: www.zerotofinals.com/learn
Multiple Choice Questions: www.zerotofinals.com/test
Instagram: www.instagram.com/zerotofinals/
Book: www.zerotofinals.com/themedicinemanual
Facebook: www.facebook.com/zerotofinals
Twitter: https://twitter.com/zerotofinals
Diuretics *Part 3* PRECAUTIONS!!! (loop, thiazides, K+ sparin
Diuretics (loop, thiazides, K+ sparing, Osmotic) Blood Pressure Med. Volume Depletion – Captured Live on Ustream at http://www.ustream.tv/channel/simple-nursing
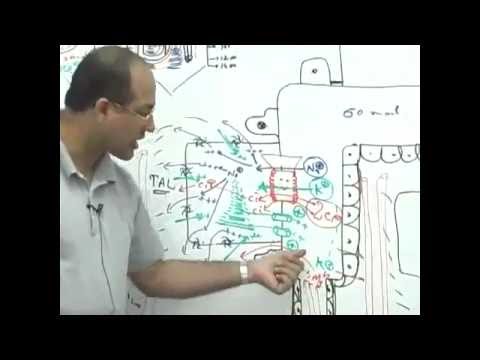
Renal Pharmacology – 01 – Review of physiology and pathophysiology
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8m_CEaRnwVI
Video lectures in clinical pharmacology by Dr. Abdel-Motaal Fouda, associate professor of clinical pharmacology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine. 2016.
foudaamm@mans.edu.eg
Pharmacology – Diuretics Simplified (Part 1)
Pharmacology – Diuretics Simplified (Part 1). This video explains the mechanism of drugs acting on PCT(proximal convoluted tubule) and nephron physiology.
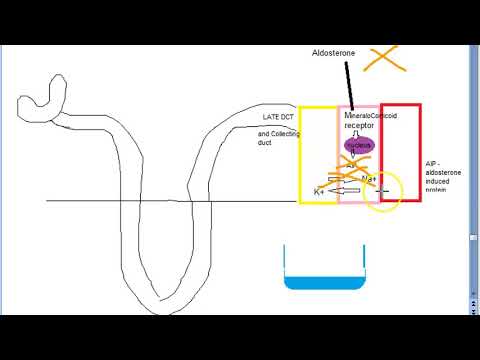
Pharmacology 652 a Potassium Sparing DiUretic Spironolactone Aldosterone antagonist Eplerenone
#PotassiumSparingDiUretic #Spironolactone #AldosteroneAntagonist Eplerenone
Diuretic (Part 08) Potassium Sparing Diuretics = Mechanism of Action (Hindi) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
(1) Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
(2) Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
(3) Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
Pharmacology – Diuretics – Part 2/3
Like this video? Sign up now on our website at https://www.DrNajeebLectures.com to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now and get 95% OFF! Get Lifetime Access for a one-time payment of $5 ONLY!
Why sign up for premium membership? Here’s why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that’s 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
Pharmacology – Diuretics (Part 2) – Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Pharmacology – Diuretics (Part 2) – Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.This video explains the important carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, their use and side effects.
Diuretic (Part- 05)Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors = Mechanism of Action (Hindi) By Solution Pharmacy
How to Download Notes in PDF from Solution Pharmacy Facebook Group Using Laptop
https://youtu.be/cE5MAt0J6hs Using Mobile https://youtu.be/ntzXKi2pA5U
Free model question paper for pharmacology 02 (5th Semester- All units) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/164xkZ5Kr5MrjiSkUykO0rHEHGl19PNKs?usp=sharing
Free Pharmacology- 2 notes (Made by students) –
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1t_nMuQEm620B8WMMgspo7swATG4LZXDe?usp=sharing
A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. Most diuretics produce diuresis by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium at different segments of the renal tubular system. Sometimes a combination of two diuretics is given because this can be significantly more effective than either compound alone (synergistic effect).
Types and Examples of Diuretics-
(1) Examples of thiazide diuretics include:
Chlorothiazide (Diuril), Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide)
Indapamide, Metolazone
(2) Examples of loop diuretics include: Bumetanide (Bumex), Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin), Furosemide (Lasix), Torsemide (Demadex)
(3) Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
Amiloride, Eplerenone (Inspra), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking following links-
Facebook Group- https://www.facebook.com/groups/solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page- https://www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
New channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) – https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCt6OXVV_2oxf5DD0Mad6e9A
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/solutionpharmacy/
E-Mail for official and other work – solutionpharmacy@gmail.com
LinkedIn- http://linkedin.com/in/pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #GPATonlinetest
Renal Pharmacology – 03 – K sparing and less commonly used diuretics
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lXp-smNY9C0
Video lectures in clinical pharmacology by Dr. Abdel-Motaal Fouda, associate professor of clinical pharmacology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine. 2016.
foudaamm@mans.edu.eg